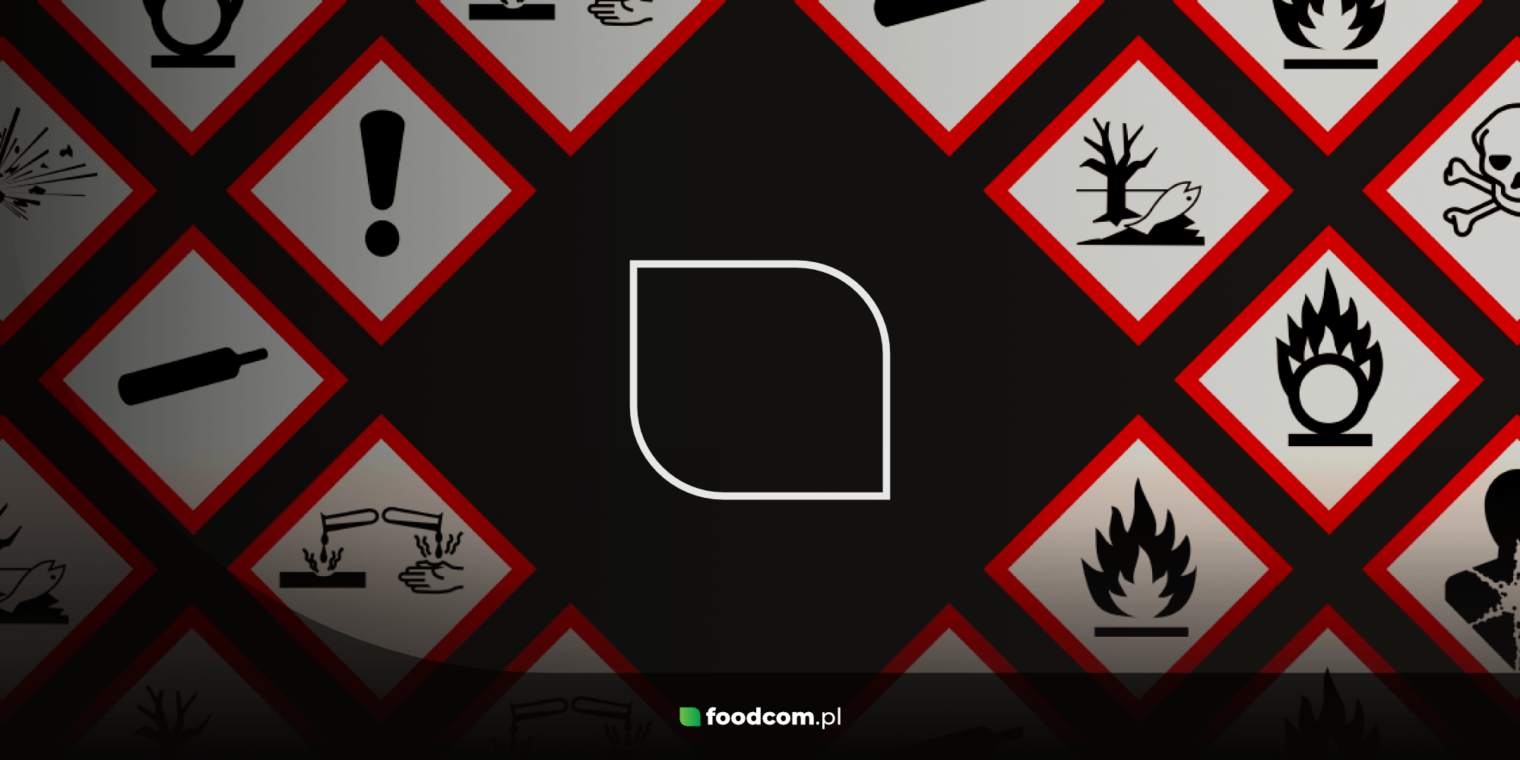
- Chemical pictograms – graphic symbols that warn of various hazards associated with chemicals.
- GHS system – an international classification system for chemicals, created by the UN, with nine pictograms describing different types of hazards.
- Safety – pictograms make it possible to quickly identify risks and implement appropriate precautions.
- Education – awareness of the dangers of chemicals is crucial both at work and in everyday life.
Ensuring safety when working with chemicals is a very important aspect, both in industry and in everyday life. Each product is characterised by a certain type of hazard. In order to quickly inform the user of potential risks, a system of chemical pictograms was used. In this way, the type of hazard is quickly and easily identified, and appropriate safety measures are taken.
What are chemical pictograms?
A chemical pictogram is a graphic symbol designed to warn users of potential hazards. The aim is safety and to reduce the risk of exposure to harmful chemicals. These pictograms are part of the GHS (Global Harmonised System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals), developed by the United Nations. Each chemical pictogram is a white rhombus with a red border, within which is a black symbol indicating the type of hazard.
Types of chemical pictograms and their meaning
There are nine basic chemical pictograms in the GHS system, each of which refers to a specific type of hazard. We discuss each type of pictogram and its meaning below.
Explosive
This pictogram indicates that a substance may be explosive. It is a warning against materials that may undergo a violent, uncontrolled chemical reaction leading to an explosion. Such substances require special care and are strictly controlled.
Examples of substances: nitroglycerine, dynamite, certain types of pyrotechnic powders and mixtures.
Oxidising substance
This pictogram indicates oxidising substances, i.e. substances that can cause or accelerate a fire. They can react with combustible materials, increasing the risk of fire.
Examples of substances: hydrogen peroxide, ammonium nitrate, perchlorates.
Flammable substances
This is one of the most common warnings, indicating that a substance is flammable. Substances marked with this pictogram may ignite on contact with air or other substances, creating a risk of fire.
Examples of substances: petrol, ethyl alcohol, methane.
Gases under pressure
This pictogram indicates compressed, liquefied or dissolved gases under pressure. There is a risk of explosion if the cylinder is damaged or if the gas is released violently.
Examples of substances: compressed oxygen, propane, liquefied nitrogen.
Toxic substance
This pictogram indicates the toxicity of the substance when swallowed, inhaled or in contact with the skin. Substances marked with this symbol may be hazardous to health or even life.
Examples of substances: potassium cyanide, arsenic, methanol.
Irritant
Indicates substances that may cause irritation to the skin, eyes or respiratory tract. Substances marked with an exclamation mark may cause allergic reactions, irritation or toxicity at high exposure.
Examples of substances: certain cleaning products, chlorine, detergents.
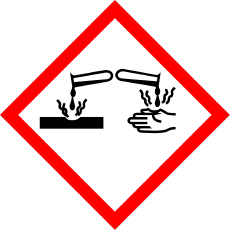
Corrosive/corrosive substances
The pictogram refers to corrosive substances that can damage metals, skin and eyes. Such substances can lead to serious injury or damage to materials.
Examples of substances: sulphuric acid, sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), hydrogen chloride
Carcinogenic/mutagenic substance
This pictogram refers to substances that may have long-lasting harmful effects on health, can cause cancer, genetic mutations, lung damage or other chronic diseases.
Examples of substances: benzene, asbestos, nicotine.
Dangerous for the environment
This pictogram indicates substances hazardous to the environment. This means that these substances can cause long-term damage to the aquatic ecosystem.
Examples of substances: mercury, mineral oils, certain pesticides.
Why are pictograms so important?
Chemical pictograms are not only mandatory but also crucial for occupational safety and health protection. They make it possible to recognise hazards quickly and to take appropriate precautions. In the event of an accident, i.e. a chemical spill, the pictograms help rescue workers and crisis management services to take appropriate action. It is worth remembering that the presence of a pictogram on a product obliges the user to consult the material safety data sheet. There you can find detailed information on risks, safety procedures and how to deal with accidents.
Education and chemical pictograms
Chemical pictograms are an indispensable part of education to prevent accidents at work and protect health. In schools, or on courses, students are educated in health and safety, chemistry, engineering or environmental protection. This knowledge is important not only in professional life, but also in everyday life. With it, we minimise the risk of mistakes. Which can result in death or serious injury. Education makes people working in industry, laboratories or other sectors aware of the risks. This knowledge can save lives or health.
Chemical pictograms are graphic symbols used to quickly communicate the hazards of chemicals. They are part of the international GHS system, created by the UN. It classifies chemicals and labels them with nine basic pictograms in red rhombuses with black symbols. Each pictogram indicates a different hazard, i.e. explosive, flammable, toxic, corrosive, carcinogenic or environmental hazard. This allows you to quickly recognise the hazard and implement appropriate safety measures. Education is crucial in work or everyday life. It increases awareness of potential hazards. It helps prevent accidents and protect human health and the environment.