- Calcium carbonate occurs in nature in the form of limestone minerals and rocks and as a component of shells.
- It can be used to extract limestone used in construction.
- The wide use of calcium carbonate is also used in agriculture, industry and food production.
- Calcium carbonate can provide a source of calcium for the human and animal body.
- There are also well-known uses of calcium carbonate in daily life, such as cleaning.
Calcium carbonate is a substance that occurs frequently in nature, for example in limestone rocks. There are known applications of calcium carbonate in daily life as well as in industry, especially in construction and food production, agriculture and medicine. What is calcium carbonate used for? How is this substance extracted and what are its natural sources?
What is calcium carbonate?
Calcium carbonate is an inorganic chemical compound that is a salt of carbonic acid and calcium. It has the chemical formula CaCO3. This substance is a component of many minerals and calcareous rocks, such as aragonite, calcite, chalk and vaterite. It also forms the shells of oysters, snails, eggshells and pearls. Interestingly, calcium carbonate is also found outside the Earth – traces of it have been discovered on Mars, among other places, which could indicate the presence of water on this planet in the past. 4
Properties of calcium carbonate
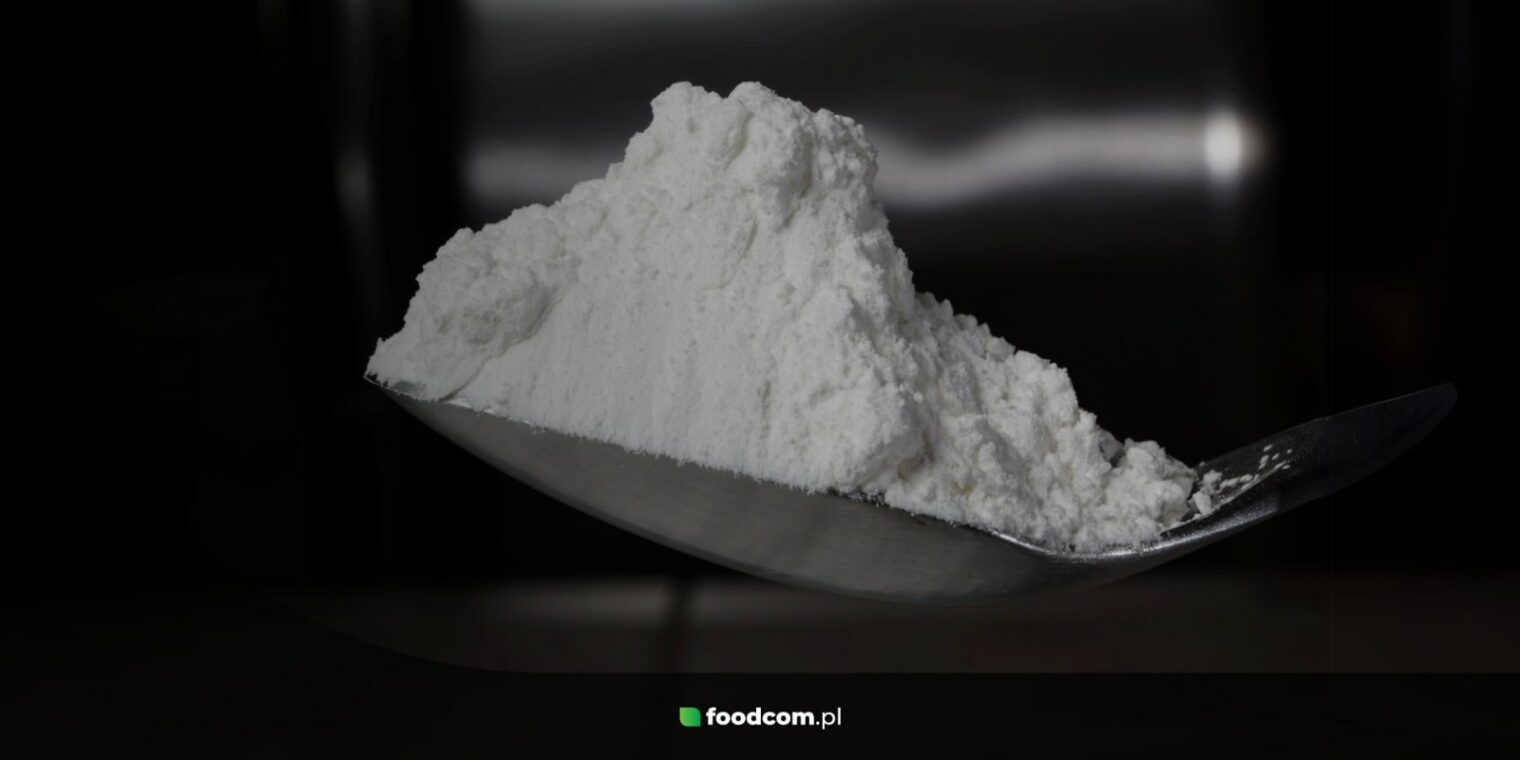
Calcium carbonate comes in the form of a white, finely crystalline powder. It has no odor and a chalky aftertaste. It can form crystalline structures. Despite its mechanical strength, calcium carbonate, which forms limestone, decomposes easily when combined with water and carbon dioxide (known as chemical weathering).
Calcium carbonate is very poorly soluble in water. In combination with carbon dioxide it forms calcium bicarbonate. It also reacts strongly with acids.
When exposed to high temperatures (above 800°C), calcium carbonate breaks down into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. This is used in calcination, which is the roasting of limestone to obtain calcium oxide (lime) for industrial use.
Calcium carbonate extraction and market
Calcium carbonate found frequently in nature. It is a component of many minerals, such as calcite or aragonite, as well as rocks: limestone, dolomite, chalk or coral. Calcium carbonate for industrial purposes is mainly obtained by mining. For applications where a high purity of the compound is required (such as in the food or pharmaceutical industry), calcium carbonate is mainly extracted from marble.
It can also be produced in the laboratory from calcium oxide and water. This is known as the carbonation process, which produces precipitated calcium carbonate. In chemistry, calcium carbonate can also be obtained by the crystallization of calcium chloride.
Nowadays, calcium carbonate is replaced by synthetic substances in some applications, such as in the manufacture of optical instruments. The reason for this is the insufficiency of existing deposits of transparent forms of calcium carbonate. More common limestone, on the other hand, is still found in large quantities all over the world: in the USA, South America, Southwest Africa, Europe (Greece, Austria, Great Britain, Italy, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Russia, Alps). Limestone is found in large quantities in Poland, especially in the south of the country.
Uses of calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a compound with a wide range of applications. It is not only used in our homes or in agriculture, but is also used extensively in construction, medicine and industry.
Application in construction
There is no doubt that calcium carbonate is most commonly used in construction. Limestone is used as a building block (e.g. sand-lime brick), and marble is also used for this purpose. Limestone aggregates are also used for road construction. Calcium carbonate is also a raw material for lime, concrete, cement or mortar, which is used as a binding agent in construction.
Very finely ground limestone rocks are used as a white colorant (known as Vienna white) and as a component of construction films. Calcium carbonate is also used in the manufacture of PVC pipes and cables (calcium carbonate increases the stiffness of polypropylene compounds) as well as emulsion paints, adhesives, sealants and fillers. For example, adhesives for ceramic tiles contain 70-80% limestone.
Calcium carbonate is used extensively in the glass and glazing industry. In ceramic-related applications, it is known as a bleaching agent.
Use in agriculture
In agriculture, calcium carbonate is used as a component of fertilizers to fertilize the soil and improve its properties. They deacidify the soil and raise its pH value. Calcium improves the physical, chemical and biological properties of the soil.
Calcium fertilizers improve the assimilability of phosphorus for the plants, which affects their growth and thus increases the yield or improves the properties of the fodder produced. Soil liming also has a positive effect on biodiversity and increases the number of microorganisms present, which have a positive effect on the soil. It also accelerates the mineralization of nitrogen and reduces the absorption of substances that are harmful to plants, such as potassium, manganese, aluminum, cadmium, nickel or zinc.
Calcium carbonate is also used in animal husbandry. Compound feed often contains the addition of this compound to supplement the animals’ diet with calcium, both for cattle and poultry. A sufficient calcium content strengthens the animals’ bodies against weakness, disease and acidosis. In dairy farming, acid calcium carbonate is used to stimulate lactation and strengthen the digestive system.
Use in the food industry
In the food industry, calcium carbonate is often used as a chemical food additive (E170). It is harmless in the quantities found in food, while excessive quantities can lead to intestinal problems.
Calcium carbonate is used in food as a hardener, acidity regulator, stabilizer, anti-caking agent and white colorant. We find it in baked goods and confectionery: Cookies, sweets or ice cream as well as in vegetable concentrates, flours and baking powders. It can also serve as a color fixative for foods (such as organic apples)
Calcium carbonate is also used as a raw material for refining sugar from sugar beet. It is also sometimes used as an additive to plant milks to enrich them with easily digestible calcium, and it is used as a deacidifying agent for wine and fruit pulp.
Uses in medicine and pharmacology
In medicine and pharmacology, calcium carbonate is used as an ingredient in dietary supplements to supply the body with calcium, for example to prevent osteoporosis, relieve muscle cramps and tremors in the legs or combat allergies. Calcium supplied in this form is about 30% absorbable. It is also used as an inert filler for tablets and other medicines and as an ingredient in vitamin pills.
Calcium carbonate is also contained in medicines intended to alleviate the symptoms of heartburn or reflux. Its effect is only an aid and consists of neutralizing the hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
Another use of calcium carbonate in medicine is to administer it to patients with hyperphosphatemia, such as patients with chronic kidney failure who are undergoing hemodialysis. When administered in this way, the preparation effectively binds phosphate and thus improves the patient’s condition. Calcium is also good for heavy metal salt poisoning.
Calcium carbonate in daily life
In everyday life, calcium carbonate is often used as an ingredient in household pastes or cleaning powders. It has excellent scrubbing properties with a low degree of hardness, so it can safely scrub many surfaces such as glass, ceramics and metal. Calcium carbonate in the form of a paste of deionized water is also used to clean silver.
Other uses for calcium carbonate
- Calcium carbonate has many other uses. For example, it is used
- in cosmetics, such as face powders, eye shadows and powders;
- in bleaching agents, white paints and powders;
- in toothpaste;
- in cigarettes;
- in jewelry making – for example, aragonite is sometimes used as a gemstone for making jewelry;
- in water treatment technology – calcium carbonate increases the alkalinity of water and binds aggressive carbon dioxide;
- in the chemical industry;
- in the petroleum industry and in the purification of iron ores;
- formerly as a component of blackboard chalk, nowadays – in paper production;
- as a component of microporous film in diapers and latex gloves;
- as a filler in thermosetting resins;
- in the energy industry to desulphurize flue gasses in order to reduce the harmfulness of their emissions;
- transparent types of crystalline calcite are used in the glass and fine ceramics industry and are also used in the manufacture of optical instruments (so-called polarizers), including in polarizing microscopes.
The role and importance of calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is one of the most important chemical raw materials. It not only has a wide range of applications in industry and everyday life, but also plays an important role in the environment.
A large amount of calcium carbonate is contained in broccoli and kale, making these vegetables an excellent source of calcium for the body. Calcium is an essential element for everyone. It serves as a building material for bones and teeth and is involved in many processes in our body, such as blood clotting, proper functioning of the nervous system, muscle work and hormonal regulation.
Calcium carbonate also plays an important role in the environment. The calcium carbonate contained in the soil stabilizes the pH value of excessively acidic soils. This compound enters the soil naturally via rocks and minerals, the shells of animals such as snails and is also produced by earthworms. These animals have special glands that convert calcium and carbon dioxide into calcium carbonate, which they then excrete into the soil.
Calcium carbonate also plays an enormously important role in the formation of fossils through what is known as calcium carbonate pre-mineralization. This has enabled the preservation of fossils for thousands of years.
We can also see the importance of calcium carbonate when we look back in time. Transparent calcite crystals, the so-called Icelandic spar, enabled the microscopic examination of rocks. They also played an important role in the discovery of the phenomenon of the birefringence of light and its polarization, as well as in the invention of the prism.