- Potato protein is a high-quality source of protein with an amino acid profile similar to that of animal products.
- It is an economical and functional alternative to traditional protein components in feed, such as fish meal or soybean meal.
- Potato protein is safe, easily digestible and also suitable for young and sensitive animals.
In an era of increasing pressure for efficiency, sustainability and cost optimisation in animal husbandry, feed manufacturers are increasingly looking for alternatives to traditional protein ingredients. One of the most promising options is potato protein, a by-product of the starch industry, which can successfully replace animal proteins in many feed applications due to its nutritional and technological properties.
What is potato protein?
Potato protein is a product derived from the processing of potatoes, specifically from the starch extraction process. It is a dry powder, usually grey or yellowish in colour, with the characteristic smell of dried potatoes. Thanks to modern purification and drying methods, the final product is free of impurities and its protein content is up to 80%.
Potato protein is characterised by:
- high biological value,
- good digestibility (approximately 70% digestibility),
- a rich profile of essential amino acids such as lysine, threonine, methionine and tryptophan.
It is the content of these key amino acids that makes potato protein perform better than many other plant proteins and only slightly inferior to animal proteins.
What is the production process for potato protein?
The production of protein from potatoes is a complex process, involving elements such as:
- cleaning, steaming and peeling the potatoes;
- extraction of the starch with water, which leads to the formation of a protein slurry;
- coagulation of proteins by means of acidification of the suspension;
- drying and pulverising.
The result is a long-lasting product that, when stored properly, can retain its properties for up to 18 months. Thanks to the standardised process, the potato protein retains its homogeneity and high quality for a long time, which is of great importance for feed manufacturers.
Advantages of using potato protein in feed
Protein is one of the most important components of animal feed, which is responsible for, among other things, the growth of their muscle mass. The high cost of the most prized animal protein means that farmers often look for alternatives in the form of plant proteins. The one derived from the potato carries a number of different benefits.
Nutritional value
The greatest advantage of potato protein is its excellent amino acid composition. The lysine or threonine content is significantly higher than in rapeseed or soya meal, making it an ideal feed component for piglets, poultry, calves, young ruminants and pets.
Low allergenicity
Unlike animal proteins or some plant proteins (e.g. soya), potato protein is not considered a strong allergen, making it safer to use – especially in young or sensitive animals.
Functional properties
Potato protein shows very good solubility and stability in technological processes, which facilitates its use as a feed additive. In addition, it acts as a natural thickener and flavour carrier. For this reason, potato flakes and protein are also sometimes used in the food industry.
Economy and availability
From an economic point of view, potato protein is an attractive alternative to expensive zoonotic proteins (e.g. fish meal) and soybean meal. The product is cheaper, of high quality and widely available on the European market as a by-product of large potato starch production, which means stability of supply and cost predictability.
Sustainable production
The use of potato protein fits into a circular economy, in which the by-products of the food industry are not disposed of but used as feed ingredients.
Use in the feeding of different animal species
Potato protein is used as a feed additive for a wide range of animal species – whether they are required to gain a lot of muscle mass, or are sensitive or have a high demand for high-quality nutrients.
Poultry
The high content of limiting amino acids and good digestibility make potato protein an excellent choice for broiler and layer feeds. It promotes rapid muscle growth and improves meat quality.
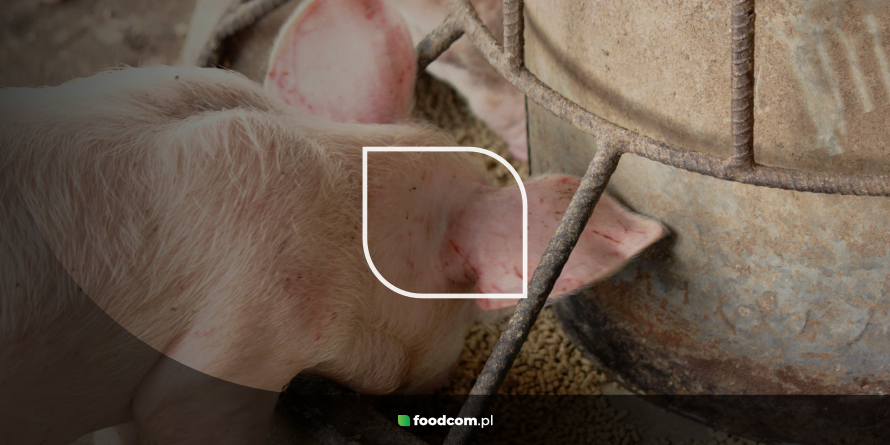
Pigs
In piglet feeds, potato protein shows high acceptability and low allergenicity reduces the risk of diarrhoea and digestive problems. Many breeders use it as a replacement for soybean meal.
Ruminants
Although the protein requirements of dairy cows or beef cattle differ from monogastric animals, potato protein can also be a valuable nutrient supplement in them. This is particularly relevant in the context of protected protein in dairy cows, which is not broken down in the rumen but is digested in the small intestine, where it is used for milk production.
Domestic animals
In dog and cat foods, especially those with food sensitivities, potato protein is increasingly replacing other sources of this ingredient, promoting good digestion and increasing palatability of feeds.
Why work with Foodcom?
Foodcom is an experienced B2B partner, offering a wide range of feed raw materials – including potato protein of the highest quality. We offer:
- comprehensive commercial service,
- logistical support,
- advice on the use of raw materials,
- stable supplies and competitive prices.
Potato protein is a versatile and valuable raw material increasingly used as an ingredient in feed production. It combines high nutritional quality with functionality and a favourable price. With the support of experienced suppliers such as Foodcom, it is possible to effectively introduce this raw material into production and achieve a competitive advantage in the market.