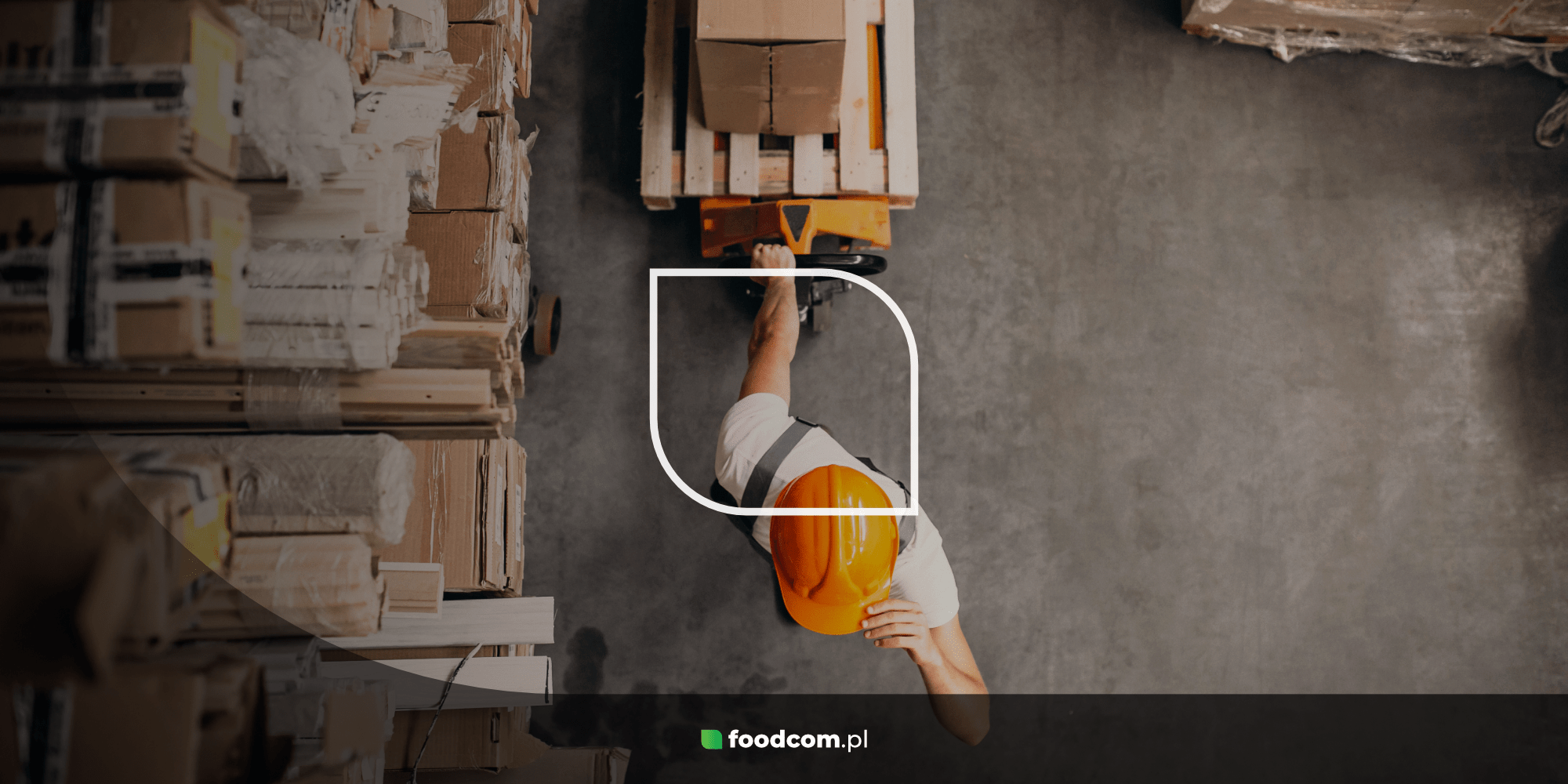
- Lead time is a key logistics performance indicator that determines the time from order placement to product delivery.
- Optimizing the lead time allows for cost reduction, increased customer satisfaction and improved delivery flexibility.
- Shortening the lead time requires automation, better cooperation with suppliers and optimization of transportation and warehousing.
- Foodcom S.A. effectively reduces the lead time thanks to IT system integration, strategic partnerships and precise demand forecasting.
In today’s dynamic business environment, time has become one of the most valuable resources. In logistics, one of the key performance indicators is lead time, or order delivery time. From the moment the customer places the order to the delivery of the product, lead time covers all stages of the logistics process. We take a look at its importance for the supply chain and how Foodcom S.A. optimises this process to achieve a competitive advantage.
What is lead time?
Lead time is the total time it takes to fulfil an order. From the moment it is placed until the product is delivered to the customer. Depending on the industry and the specifics of the processes, lead time can involve different stages:
- Order processing time – the period of time from when the order is placed to the start of processing.
- Production time – in the case of custom-made products, this is the time it takes to produce the goods.
- Delivery time – the period from the end of production or preparation of the goods to their delivery to the customer.
- Transport time – for international deliveries, this time can be significantly increased due to international logistics.
In logistics, lead time is often divided into internal (the time it takes to process an order within a company) and external (the time associated with delivery from a supplier or to a customer).
How do you calculate lead time?
Calculating lead time requires an analysis of each stage of the logistics process. For example, if an order consists of the following steps:
- Order placement – 1 day
- Order processing – 2 days
- Production – 5 days
- Packing and preparation for dispatch – 1 day
- Transportation – 3 days
The total lead time in this case is 12 days. To calculate the lead time accurately, other factors must also be taken into account:
- Availability of raw materials – lack of materials can increase production time.
- Transport delays – logistical problems such as traffic jams, strikes or weather conditions can affect delivery times.
- Seasonality – during periods of increased demand (e.g. holidays) lead time may increase due to a higher number of orders.
Importance of Lead Time in Logistics
Lead time affects the supply chain and the competitiveness of companies. The benefits of optimising this indicator.
- Flexibility – shorter delivery times allow companies to respond much faster to changing market demands
- Cost reduction – faster fulfilment means lower inventory. This translates into lower storage and warehouse management costs.
- Increased customer satisfaction – faster delivery of goods influences good customer relations. This leads to increased customer loyalty
- Minimising danger – reduces the danger associated with old stock.
How do you optimise Lead Time?
Optimising lead time requires a comprehensive approach and collaboration across multiple levels of the supply chain. Here are some effective strategies:
- Process automation: Introduce IT systems such as ERP or WMS. These allow for faster order processing and better inventory management.
- Working closely with suppliers: Building long-term relationships with suppliers and jointly planning deliveries can significantly reduce lead times.
- Transport optimisation: Selecting efficient means of transport and optimising delivery routes can reduce delivery times.
- Demand forecasting: By analysing historical data and market trends, companies can better plan production and deliveries, avoiding delays.
- Lean management: Implementing lean management principles, such as the elimination of waste and continuous process improvement, can help reduce lead times.
Case Study: Foodcom S.A.
Foodcom S.A., a company operating in the food industry. It is well aware of the importance of lead time optimisation. In the case of food products, delivery time is crucial.
Foodcom S.A. has implemented a number of solutions to reduce lead time:
- IT systems integration – the company uses advanced systems to manage orders and track deliveries in real time.
- Close collaboration with suppliers – Foodcom S.A. has established strategic partnerships with local suppliers. This has allowed the company to reduce delivery times for raw materials.
- Optimisation of warehouse processes – the introduction of a WMS system has enabled faster order picking and reduced errors.
- Demand forecasting – by analysing historical data, the company is better able to plan production and deliveries.
Lead time is a key indicator in logistics. It has a direct impact on supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Its optimisation requires a comprehensive approach. It includes process automation, collaboration with business partners and data analysis. The example of Foodcom S.A. shows that reducing lead time is possible and can bring tangible benefits to the company.







![Butter Market Overview in 2026 [Global Report] Butter Market Overview in 2026 [Global Report]](https://foodcom.pl/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/global-report-maslo-600x300.png)


