- Carob comes in various forms – powder, paste, syrup, or “chocolate chips”.
- It contains less protein and fat than cocoa, has no stimulants and fewer calories, and has a naturally sweet taste.
- Carob can be found in various types of diet products, products for diabetics or athletes. It can also be used as a substitute for cocoa in the kitchen.
In the search for new, healthy versions of familiar and well-loved foods, we are increasingly turning to alternatives. One of these is carob, one of the products that are equally healthy substitutes for cocoa, which is gaining increasing popularity both in the industry and among consumers. What exactly is carob? What are its properties and in which cases should it be considered as a substitute for cocoa?
What is carob?
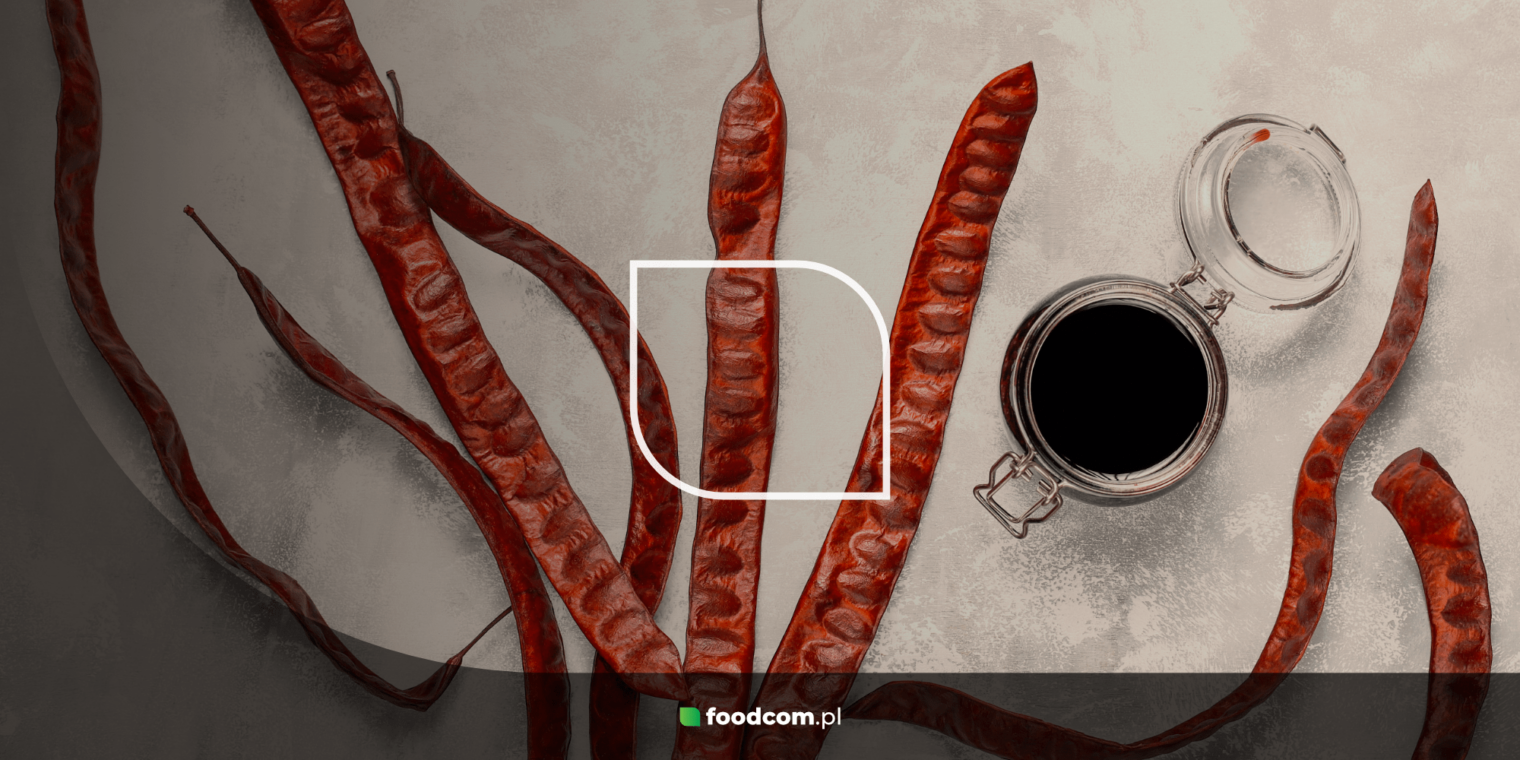
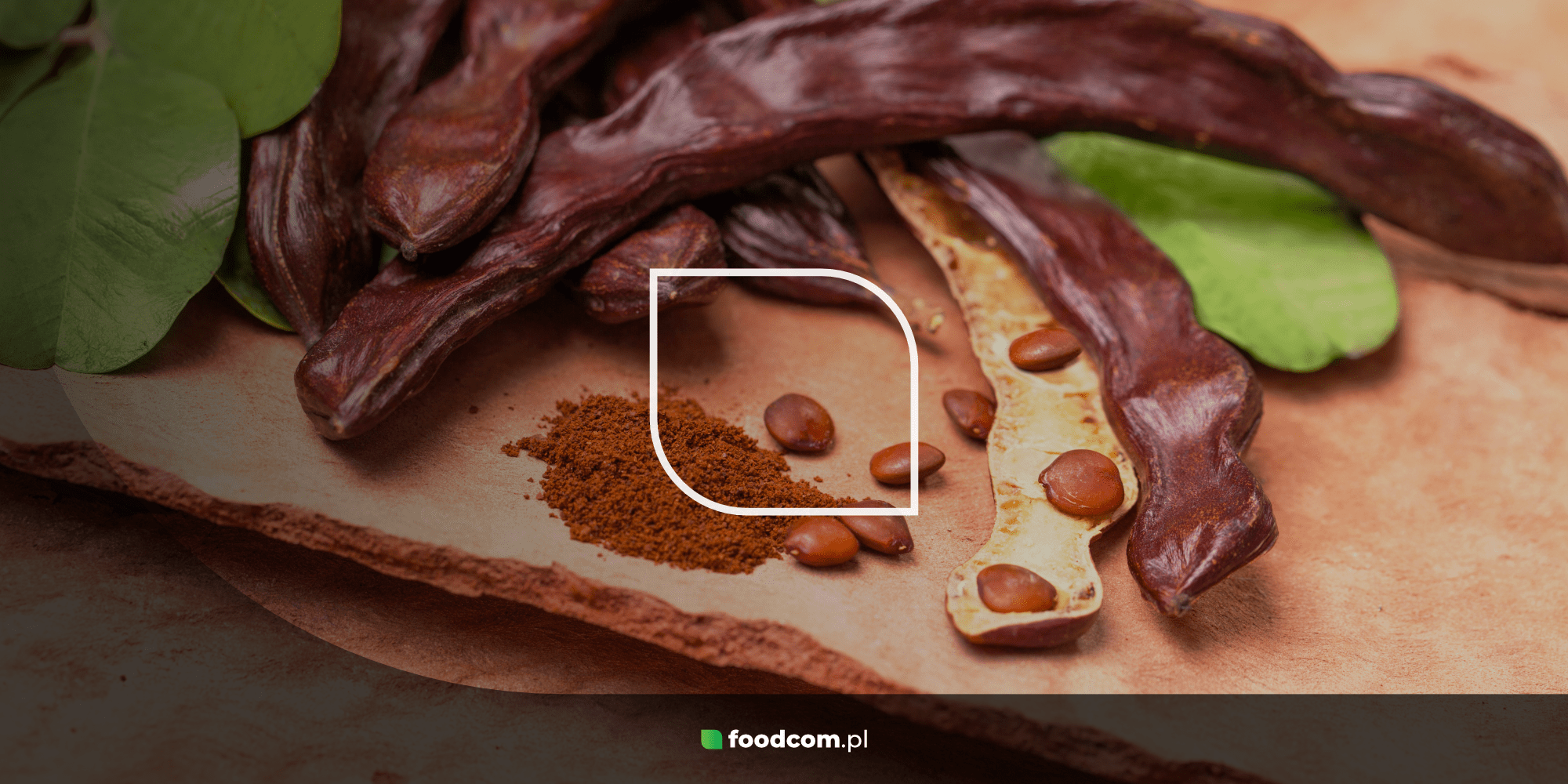
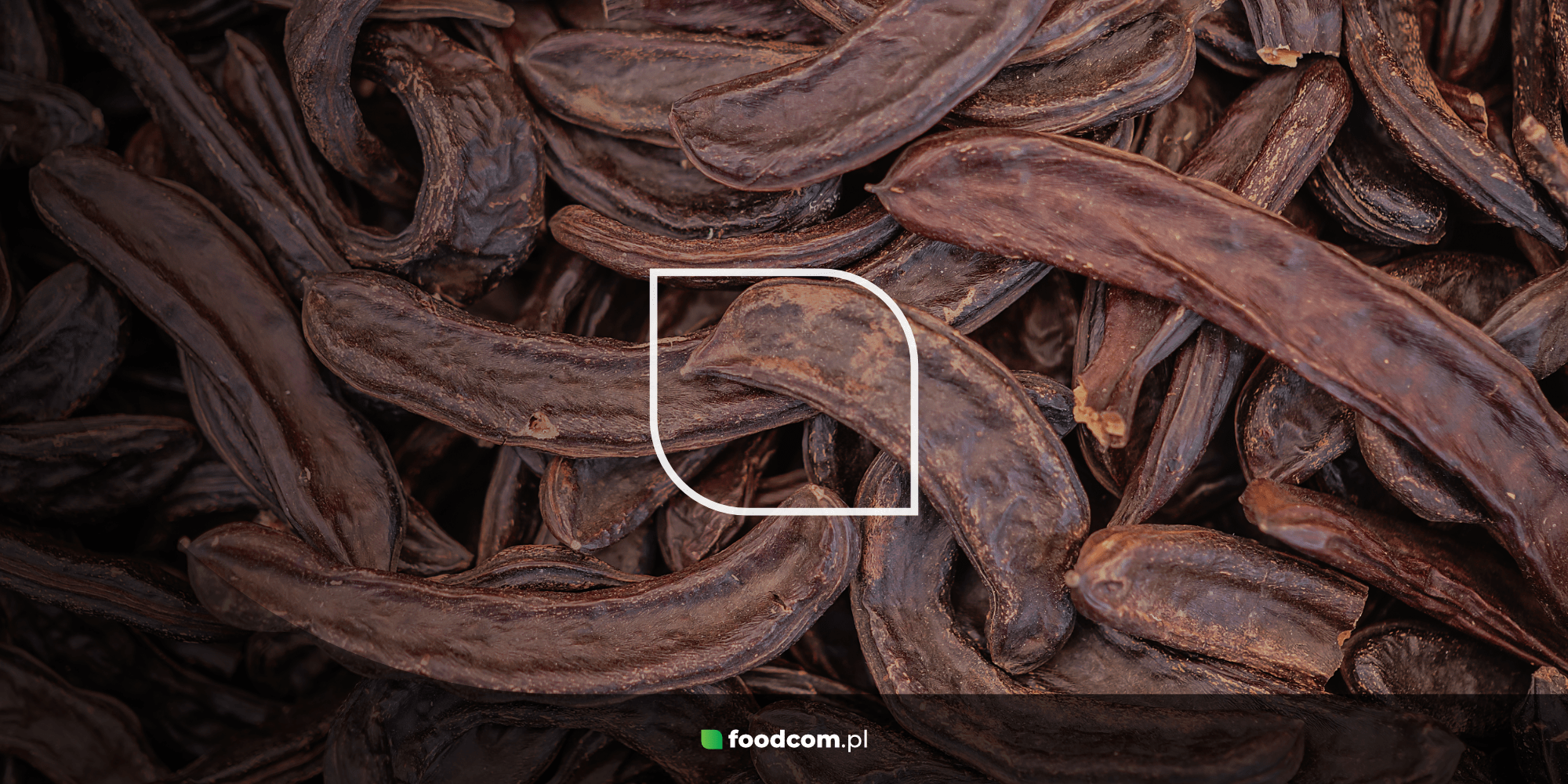
Carob is a powder extracted from the fruit of the carob tree, also known as the carob pod (Ceratonia siliqua), which grows mainly in the Mediterranean region. The ripe fruit of the tree in pod form is dried and ground to produce a powder, often called carob flour. Chocolate-like pieces of carob can also be obtained from the pods. The ground endosperm of the seeds, on the other hand, is used to produce locust bean meal, which has no particular taste and is a technological food additive to help thicken products.

Properties of carob
Carob can come in the form of powder, pieces resembling chocolate ‘chips’, paste, syrup or dried fruit. Carob is undoubtedly a dietary ingredient beneficial to our health. It is an excellent source of dietary fibre, which supports the digestive system and helps regulate blood sugar levels. It also contains numerous polyphenols – compounds with antioxidant properties, as well as minerals (calcium, magnesium, potassium, iron) and vitamins, especially from the B group – essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system.
Carob is naturally sweet – its sweetness is estimated at ⅓-½ the sweetness of sugar. It is therefore an ideal ingredient for sugar-free desserts, baked goods, smoothies or snacks. Compared to cocoa, carob also contains significantly less fat. Companies such as Foodcom S.A., which specialises in supplying raw materials and intermediates to the food industry, offer carob as an alternative ingredient to cocoa with growing popularity.
Carob and cocoa – similarities and differences
Both carob and cocoa are used as ingredients in chocolate products, desserts and beverages. Their appearance and use are similar, but in terms of properties they differ significantly.
Alkalized and non-alkalized cocoa, unlike carob, contain stimulants in the form of caffeine and theobromine. These ingredients are not found in carob, making it safe for pregnant women or children, who should avoid the stimulating properties of classic cocoa.
The taste of cocoa is quite bitter and intense, and sugar or other sweeteners are usually added to recipes using it. Carob, on the other hand, has a naturally sweet, caramel-like aftertaste, so it can be used on its own without sweetening to mitigate the bitterness. Together with its lower fat content than cocoa, this makes carob extremely attractive to manufacturers of healthy functional foods.
In terms of nutritional value, both cocoa and carob are products that contain substances that are beneficial to health. Cocoa has more protein, potassium and magnesium in its composition than carob, while this one is more rich in calcium. It is also twice as low in calories as cocoa and contains less fat, including saturated fat. Both products contain large amounts of antioxidants, which protect blood vessels and counteract inflammation in the body.
Carob applications – in industry and in the kitchen
Carob is a product with a rich tradition. In the Mediterranean, the plant has been used for many years as a sweetener and flavouring, producing sweet syrup or traditional snacks. It was also used as animal feed and as an ornamental plant. Where is carob used today?
Food industry
Carob in its various forms is used in the food industry, including:
- candy bars
- vegetable drinks,
- baked goods,
- dietary snacks,
- toppings,
- ice cream.
Due to its stabilising properties, locust bean gum is sometimes used as a food additive – a natural thickener, e.g. in jams and jellies.
Carob is particularly attractive to consumers who are intolerant to or avoid caffeine. Its low calorific value, low glycaemic index and low fat content make carob a good product for people watching their weight and diabetics. It does not contain gluten or lactose, so it will also be a good alternative for allergy sufferers – especially those who are allergic to cocoa products. When choosing carob, however, it is important to bear in mind its naturally sweet taste – when substituting cocoa, use the same amount of carob, but less of the sweetener.
Feed industry
Carob and locust bean meal are also sometimes used in the production of animal feed. Carob is used both for the production of energy-rich feed for livestock, mainly ruminants, and for canned dog food and treats.
Other uses
Carob is not only used in food, but also in the cosmetics, cigarette and even paper industries. Carob pods are also sometimes used to make sweet liqueurs or alcoholic liqueurs, as well as an alternative to coffee.
Carob is not only a trendy superfood, but above all another healthy alternative to cocoa, which is used both in the home kitchen and in the food industry. Thanks to its unique properties, carob is increasingly becoming an ingredient in dietary, functional and health-promoting products.